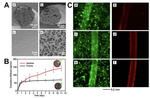
Abstract:
One of the biggest challenges within the medical practice is the innovation and improvements in technologies for the closure of wounds or sutures. The general technologies comprise physically perforating materials, for example, staples or sutures. These approaches have several limitations and challenges such as the risk of infections, cause continues pain, not always effective and in some cases can result in leakage at the site of closure. To overcome these challenges and limitations polymer-based sutures can be employed to hold body tissues together or ligate blood vessels, after a surgery or accidental injury. Depending on the damaged site, specific features are required to withstand the natural conditions of the body, but the utmost property for a suture material is its tensile strength, which can be tailored by the composition and thickness of the yarn. Aside the strength, other important properties to be considered are absorbability, sterility, high knot security, lack of allergic reaction, and ease of handling. In addition to these characteristics of biomaterials, in general, other criteria used for suture selection are based on the properties of the tissues involved, such as the specific healing rate; wound condition and general health of the patient, potential postoperative complications, personal preference and experience of the surgeon, and economic reasons. Among the extensive portfolio of materials currently available, synthetic and natural polymers have been the most frequently targeted.

